Suntan With Coated Potentiometers and Wire-Wound Potentiometers
Previous blog we talk about Potentiometers by means of construction, they can be divided into 2 groups: coated and wire-wound. Now let us to to know more related details of it.
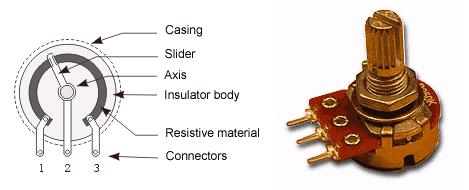
With coated potentiometers, (as shown follow figure), insulator body is coated with a resistive material. There is a conductive slider moving across the resistive layer, increasing the resistance between slider and one end of pot, while decreasing the resistance between slider and the other end of pot.
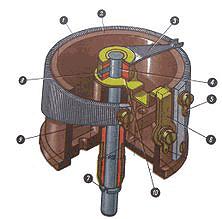
Wire-wound potentiometers are made of conductor wire coiled around insulator body. There is a slider moving across the wire, increasing the resistance between slider and one end of pot, while decreasing the resistance between slider and the other end of pot. Wire-wound potentiometers are used in devices which require more accuracy in control. They feature higher dissipation than coated pots, and are therefore in high current circuits. Construction of a wire-wound circular potentiometer (as shown follow figure). The resistive element (1) of the shown device is trapezoidal, giving a non-linear relationship between resistance and turn angle. The wiper (3) rotates with the axis (4), providing the changeable resistance between the wiper contact (6) and the fixed contacts (5) and (9). The vertical position of the axis is fixed in the body (2) with the ring (7) (below) and the bolt (8) (above).
Coated pots are much more common. With these, resistance can be linear, logarithmic, inverse-logarithmic or other, depending upon the angle or position of the slider. Most common are linear and logarithmic potentiometers, and the most common applications are radio-receivers, audio amplifiers, and similar devices where pots are used for adjusting the volume, tone, balance, etc..
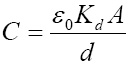
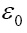 is the dielectric permittivity of vacuum, Kd is the dielectric's dielectric constant and d is the distance between the two plates.
is the dielectric permittivity of vacuum, Kd is the dielectric's dielectric constant and d is the distance between the two plates.