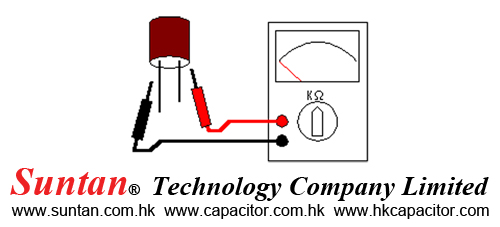
Suntan Technology Company Limited
----All Kinds of Capacitors
Desalination could dramatically help the looming shortage with water. The problem is the membrane.
Right now, desalinting seawater largely revolves around pressurizing water and forcing it through a membrane to purify it. The process takes a lot of energy and hence a lot of cost. Desalinating seawater can cost as much as 50 cents a liter.
A collection of private companies and research institutes in Spain have begun to experiment with capacitive deionization for purifying seawater. In this, two electrodes would be placed in a tank. The ions (i.e., salt particles) would be drawn to one electrode. The ions would absorb the ions, which could then be released in a regeneration cycle. Capacitive purification was considered in the past, but the materials were too expensive. So who knows, it might work now.
Expect to see a number of desalination come to the fore in the next few years. Policy makers and the public love the idea and areas of Australia, Africa and China are already suffering through prolonged droughts.
Some of the more interesting ideas out there:
Porifera: A spin-out from Lawrence Livermore National Labs, the company wants to make a desalination membrane out of carbon nanotubes. The company claims it won’t take much energy to purify water in this way and the membrane can’t get fouled. Salt and other bad stuff can’t fit through the pore/openings in the nanotubes.
NanoH2O: Grew out of a research project at UCLA and so far has raised $20 million in two rounds. It has a membrane embedded with nanoparticles that repels salts and lets water pass. By exploiting chemical attraction, NanoH2O reduces the amount of mechanical-induced pressure required for reverse osmosis: The company claims it can process 70 percent more water with 20 percent less power than conventional reverse osmosis plants.
Quos: A highly secretive Chicago company founded by Chinbay Fan and funded by Khosla Ventures. One thing Quos can’t keep secret: patent applications for a system that desalinates and purifies with graphite porous electrodes.
“The apparatus is capable of removing ionized and non-ionized organic compounds, inorganic ions, particulates and bacteria from wastewater streams in a single unit to produce potable water. Porous carbon-based electrodes function as impurities filters to remove particulate matter, such as ash, sand and high molecular weight compounds, as electrodes to concentrate and remove ionic species, and as adsorbents to remove organic materials and bacteria from the wastewater stream,” says patent application 11/724534.
Stonybrook Purification: It has created a thin, fibrous scaffold for reverse osmosis membranes that increases water flow to the reverse osmosis membrane. The company, out of SUNY Stony Brook, also has its own reverse osmosis membrane.